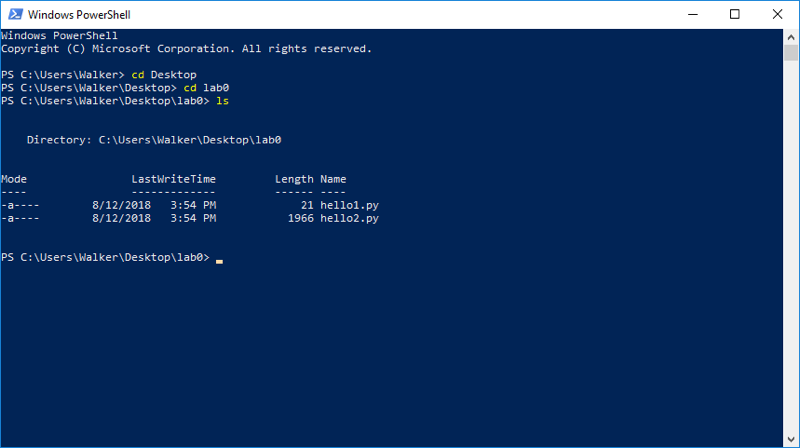
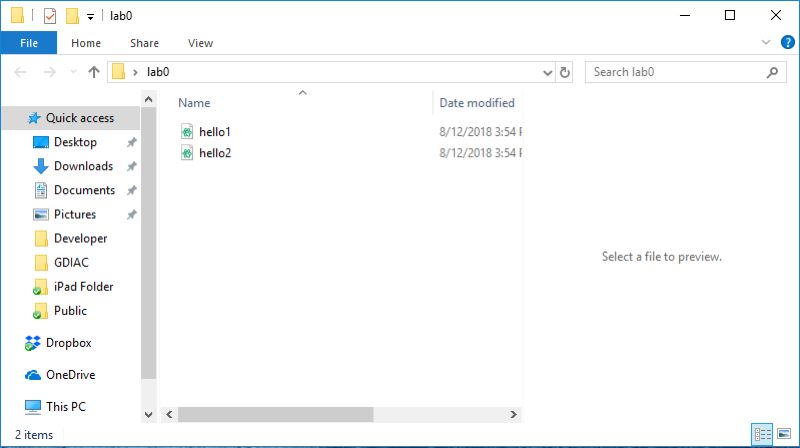
A command shell can be thought of as a combination of (a) a text-based version of a file manager and (b) a place where one can type commands to be executed. At any given time it is open to a specific folder (or directory) on your computer. We call the folder that is currently open in the shell the working directory. The pictures below show a command shell and a graphical file manager with the same working directory.
| PowerShell window | Explorer window | |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
Every computer user has what is known as a home directory. This is the folder that has your name. In Windows 10, this is a hidden folder which contains all your other folders, like Downloads or the Desktop. Whenever you open a new command shell, it always starts in the home directory. As your homework and lab assignments will often be in different folders, the first thing you need to learn about the command shell is how to change directories. That is the focus of the tutorials below.
In Windows, the command shell is called the PowerShell. There is another, older command shell called the Command Prompt. However, official Microsoft policy since Windows 10 is to use the newer PowerShell, and that is what we recommend. It is much closer to the MacOS and Linux versions we show in class, and so you will be less confused.
To find the PowerShell, just search for “PowerShell” in the search box at the bottom of the Start Menu. When you start up the PowerShell, you get a Window that looks something like the illustration below. At any given time, the bottom line of the PowerShell is the working directory followed by a > symbol.
To get the PowerShell to do something, simply type in a command, and hit Return.
The shell will then process the command, either doing something or printing out an error
message. When done, it will present the prompt again, ready for you to type in a new
command.
As we mentioned above, the PowerShell works like the Windows Explorer. At any given time it is open to a specific folder (or directory) on your computer, which we call the working directory.
When working on a Python assignment, you want to make sure that the working
directory is the directory that contains the .py files you are
currently editing. Many a student has found themselves editing a .py
file while testing one (of the same name) in a different folder. You might
be tempted to just put everything in your home directory. However, this is
a bad idea and as the folder will get very cluttered as the semester progresses.
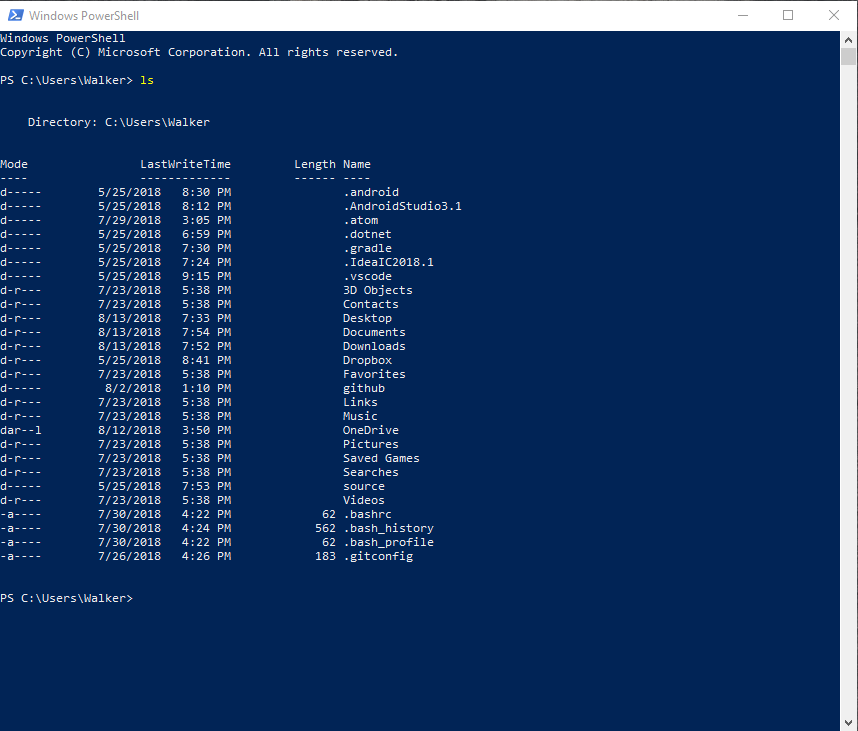
The two most important commands to know in Windows are ls and cd.
Typing in ls displays the current working directory as well
as all of its contents. An example of the ls command is shown
below.
The cd command is an abbreviation for “change directory”. It is how you move
from one folder to another. When you type this command into the PowerShell, you
must give it two things: the command cd and the name of the folder you wish to
go to. Using the example above, suppose we wish to switch the working directory to
Desktop. Then you would type
cd Desktop
Try this out and then type ls. See the difference?
There are a couple of important tricks to know about the cd command.
The simplest form cd can only move to a folder that is “sees” (e.g. is a
folder inside the working directory). If you change to directory (such as Desktop),
you can no longer see the original directory (your home directory); it is outside
of the current working directory. So how do you back-out if you go into a folder
by mistake?
The solution is that there is a special folder called ...
This refers to the folder that contains the current one. Type
cd ..
and see what happens. If you typed it just after moving into the Desktop folder (from the previous example), then you should be back in your home directory.
Combining cd .. with regular uses of the cd command are enough
to allow you to move up and down the directory hierarchy on your computer.
If you are new to the PowerShell, you might find yourself quickly getting tired of all the typing that you have to do. Particularly when you have a directory with a very long name. A slight misspelling and you have to start all over again.
Fortunately, Windows has tab completion to speed things up. Go to your home directory and type (but do not hit Return)
cd D
Now hit the tab key. See what happens? Windows turns “D” into the first folder that it can find that starts with that letter (which is likely to be Desktop, and not Documents, as it comes first alphabetically).
Suppose you are currently in the your home directory; you want to move to the folder
“Favorites” which is inside of “Documents”. You could do this with two cd commands.
But to do it with a single command, you just connect the folders with a \, as
follows:
cd Documents\Favorites
When you combine this with .., you can do some rather clever tricks.
Suppose you are currently in the Desktop directory, and you want to move in the Documents
directory (which is contained in your home directory). You can do this with the command
cd ..\Documents
We refer to these expressions as paths; they are are a “path” from the working directory to the directory that you want to go to.
The paths that we have shown you are more properly called relative paths. They show how to get from the working directory to your new directory. The correct path to use depends on exactly which directory is the current working directory.
Absolute paths are paths that do not depend on the working directory; instead they depend on the disk drive. They always start with name of the drive. For example, suppose you inserted a USB drive into the computer, and you wanted to open that drive in the PowerShell. The USB drive will (typically) be the the E: drive, so you simply type
cd E:
You can combine this with the \ symbol to move anywhere you want on the USB
stick. If the USB stick has a folder called “Python” on it, simply type
cd E:\Python
Any time that you need to change disk drives, you need to use absolute paths. If your user account is called “Sally”, then you return to your home directory by typing
cd C:\Users\Sally
The PowerShell breaks up the commands that you type in by spaces. That means that if you have a folder with spaces in the name, it will break it up into references to two different folders. For example, suppose you have a folder called “Python Examples”, and you type
cd Python Examples
You will get an error saying that Windows cannot find that path.
To solve the problem, put the directory in quotes. The following should work correctly.
cd "Python Examples"
If you are changing multiple directories then you need to put the entire path in quotes (not just the folder). For example, if you want to go to “Program Files” on the C drive, type
cd "C:\Program Files"
If you take a folder and drag-and-drop it onto the PowerShell, it will fill the window with the absolute pathname of that folder. Therefore, to quickly move the PowerShell to a a specific folder, do the following:
cd followed by a space.The PowerShell allows you to do everything that Windows Explorer can do (and more). You can use the PowerShell to make folders, move files, and delete files. However, none of this is necessary for you to learn. For this class, you never need to understand how to do anything other than navigate directories. You can do everything else in Windows Explorer (or some other program) if you wish.
To make a new folder or directory, use the command mkdir followed by the name of the
new folder. For example:
mkdir MyFolder
The new folder will appear in the current working directory.
You can also delete a directory with the rmdir command. For example, to delete the folder we just made, type
rmdir MyFolder
The PowerShell will only delete empty directories. If there is anything in a directory, it will not let you delete it. You have to delete the contents first.
You move files with the move command. The way this command works is that you give it
two file names. It searches for a file with the first file name; once it finds it, it
makes a copy with the new file name and then deletes the original.
For example, suppose you wanted to rename the file test.py to assignment3.py.
Then you would type
move test.py assignment3.py
(this by the way, illustrates why paths cannot have spaces in them).
If the second filename is path to a file, then it will move the the file into the
correct directory. For example, suppose we now wanted to move assignment3.py to
the Desktop (which is a folder in the current working directory), and rename it
`completed.py1. Then we would type
move assignment3.py Desktop\completed.py
If we want to keep the name as assignment3.py, you could shorten this to
move assignment3.py Desktop
In this case, the PowerShell will move assignment3.py into Desktop, but keep the
name of the file unchanged.
The move command will always delete the original (name of) the file when it is done.
Sometimes we want to make a copy of a file. We do that with the copy command.
Suppose that assignment3.py is in the working directory and we want to put a copy
on the Desktop without deleting the original. Then we would type
copy assignment3.py Desktop\assignment3.py
Files are deleted with the del command. In our running example, to delete the file
assignment3.py, you would type
del assignment3.py
Be very careful with this command. It completely erases the file. It does not move the file your Recycle Bin. You cannot retrieve a file deleted this way.